Pregnancy is an exciting and expectant time with lots of joy and intense experiences. It is a very special event in your life and new things are coming your way. You have many questions about your child’s development.
Here you will find an overview of the upcoming examinations. Our pregnancy schedule provides a condensed overview.
You can find more practical information about being pregnant in Munich hier.
Maternity guidelines
The statutory maternity guidelines offer you a wide range of medically necessary services. However, you and your baby will only benefit from the preventive program if you use it regularly. Continuous examinations are a prerequisite for identifying and treating risks as quickly as possible.
Maternity Policy - The Statutory Benefits
This is initially carried out at approx. 4-week intervals and later, according to the course of pregnancy, at 2-week intervals.
During the initial examination, in addition to a detailed anamnesis, the vagina and uterus are examined.
The following examinations are carried out regularly at the check-up appointments:
- Blood pressure measurement
- Urinalysis
- Weight control
- Hemoglobin determination – iron value, depending on the last finding
- Exclusion of chlamydial infection
- Blood tests
The determination is made at the beginning of pregnancy
the blood group and the Rhesus factor as well as the implementation of an antibody search test, in order to identify any blood group incompatibility between you and your child at an early stage. This antibody search test is repeated between the 24th and 27th week of pregnancy. If you have the blood group characteristic “Rhesus negative”, you will receive an injection between the 28th and 30th week of pregnancy to prevent possible intolerance.
A search test for sexually transmitted diseases (Lues search reaction – LSR) and a test for “rubella antibodies” are also required by law, unless two vaccinations or specific antibodies are detected. This is important because rubella virus infection during pregnancy can lead to malformations in your child.
We would like to recommend that you also have an examination for HIV (AIDS virus) carried out.
After the 32nd week of pregnancy, another blood sample is taken to reveal any infection with the hepatitis B virus. Such an infection could infect your child during birth.
The medical advice at the beginning of your pregnancy also includes recommendations for a healthy diet. This is for your own health and the optimal development of your child. The basis for this is the fact that there is an increased need for certain micronutrients during pregnancy, such as B .:
- Folic acid
- iodine
- iron
- Vitamin D
- Omega-3 fatty acids
Nutrition reports and surveys among women of childbearing age show a clear undersupply with these substances that are important for the development of your child. On the other hand, excessive weight gain from high-calorie foods can increase the risk of diseases during pregnancy such as diabetes and high blood pressure. You will also be informed about the relationship between diet and the risk of tooth decay.
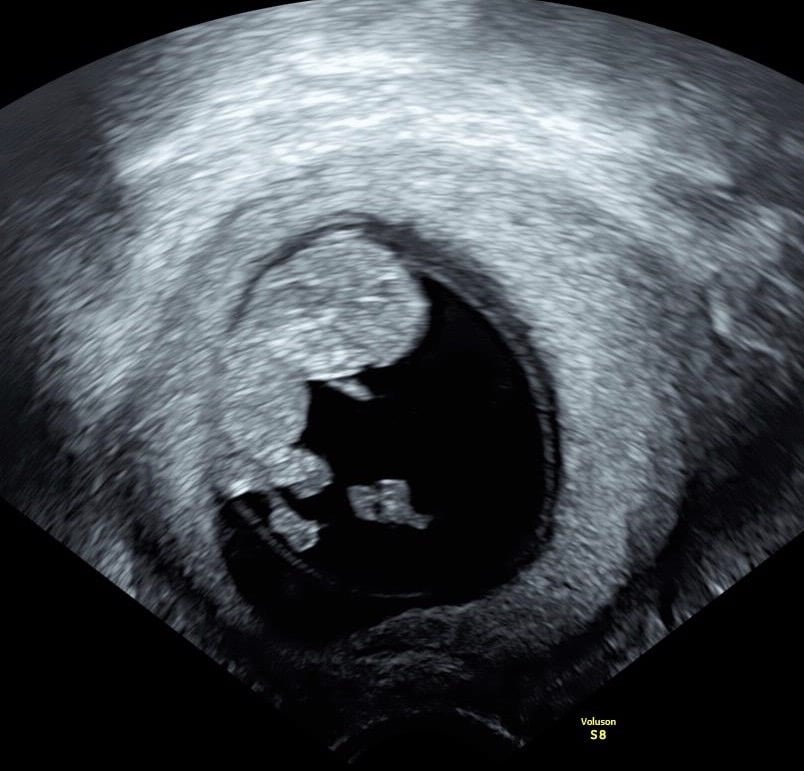
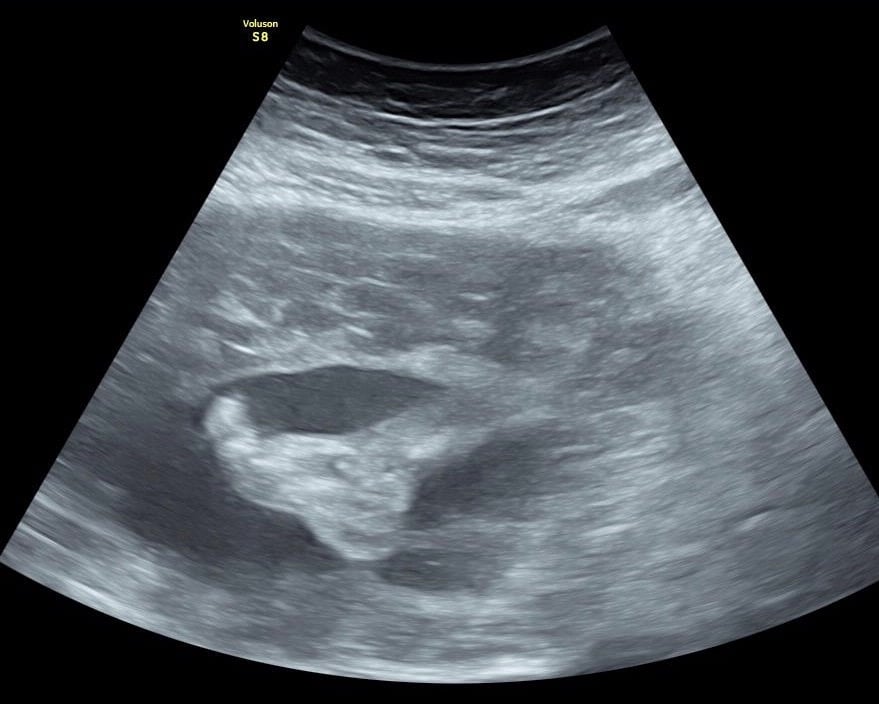
An ultrasound assessment of the child’s development is planned three times during pregnancy.
- Basic ultrasound: 9th – 12th week of pregnancy
- Basic ultrasound: 19th – 22nd week of pregnancy
With the 2nd ultrasound you can choose between two alternatives to detect any abnormalities:
a) a basic ultrasound examination
b) an extended basic ultrasound examination
- Basic ultrasound: 29th – 32nd week of pregnancy
We kindly ask you not to put lotion on your baby bump on the day of the ultrasound examination and to remove navel piercings (if any). So the conditions for the examination are optimal.
The sugar test is offered between the 24 + 0 and 27 + 6 weeks of gestation. If you decide to do this, first do a pre-test in which you drink a glass of water with 50 grams of sugar (not empty). If an increased value is found in this pre-test, a second diagnostic test will be carried out shortly, which is more complex and you have to be sober, i.e. you have not eaten or drunk anything for at least 8 hours. For this purpose, blood is drawn from a vein in your arm. Possible consequences of gestational diabetes are so-called preeclampsia or birth complications.
From the third trimester of pregnancy onwards, we regularly check your child’s heart rate and your uterus’ willingness to go into labor.
From the third trimester of pregnancy, all pregnant women are offered the standard vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) so that the unborn child receives as many antibodies as possible via the placenta and umbilical cord. In this way you can improve the nest protection of your baby after birth before it can be vaccinated yourself.
Depending on the time of year, it is recommended that pregnant women be vaccinated against the flu. The primary goal is to protect pregnant women from a severe flu infection.
Pregnancy Plus: our additional offers
In order to rule out specific infectious diseases in the mother, which can impair the child’s health and development in the event of an initial infection during pregnancy, we recommend an antibody titer test in the blood. If you do not have any antibodies, a further check later is recommended.
Toxoplasmosis
Infection occurs mainly through contact with cats (cat feces) or through the consumption of raw meat (mett or tartare, ham, salami) or meat that has not been cooked through as well as unwashed fruit, vegetables and salad.
In Germany around 45-50% of women of childbearing age have gone through this disease unnoticed and are therefore protected. An initial infection during pregnancy can cause severe malformations with brain damage and blindness in the unborn child.
By taking a blood sample at the beginning of pregnancy, we can determine at an early stage whether antibodies (defense substances) against toxoplasmosis have already been formed. If there is no immune defense, further check-ups should follow.
Chickenpox
If the mother is infected for the first time during pregnancy, congenital varicella syndrome can occur. A maternal infection around the birth can also lead to a severe infection with a high mortality rate in the newborn. If you do not have antibodies, you can take special precautionary measures during pregnancy and get vaccinated after the birth.
Cytomegaly (CMV)
Cytomegaly is the most common infection in pregnancy.
Many women in Germany were already exposed to the pathogen before pregnancy and are therefore largely protected, but the fetus is also affected in 40% of women who are infected with cytomegaly for the first time during pregnancy.
This infectious disease can also have long-term consequences: around 10% of children with the disease show symptoms, mostly of a neurological nature.
Ringlet rubella
Parvovirus B19 causes rubella, one of the five childhood diseases commonly associated with rash (measles, chickenpox, rubella, scarlet fever, rubella). The virus infects and destroys the erythrocyte precursors, causing anemia (anemia). Parvovirus B19 is transmitted through droplets or contact infections with saliva, blood or other body fluids. Women who are in contact with small children (educators, mothers of small children, etc.) are particularly at risk of infection.
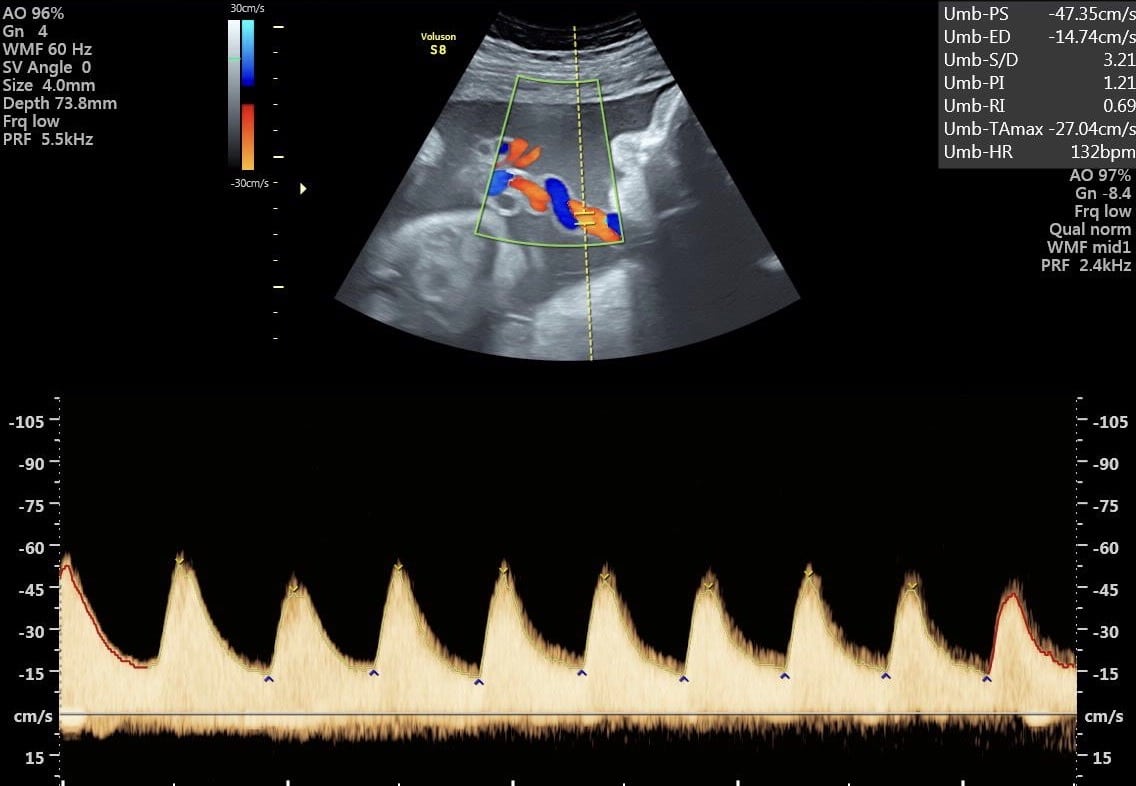
In the event of initial contact with parvoviruses during pregnancy, close monitoring by Doppler sonography must be initiated in order to diagnose fetal anemia at an early stage. Should this rare event occur, therapy options exist for the unborn child.
Hepatitis C
A hepatitis C test is usually required for water births.
Unfortunately, thyroid control is not a standard part of maternity guidelines.
It is important for your child’s development that your thyroid is well adjusted during pregnancy. In the case of pre-existing illnesses, we ask for joint care with regular controls of the parameters by your general practitioner or specialist.
If we should find that your blood type is “Rhesus negative”, you must routinely do an i.m. Syringe (Rhophlyac) given during pregnancy and after childbirth and if bleeding during pregnancy.
These injections are not necessary if the child’s father is also rhesus negative. To be on the safe side, we need a written laboratory report – your partner is welcome to have the blood test carried out by us. Just like you, he will then receive a blood group ID.
If your partner has a “rhesus positive” blood group, there is the possibility of determining your child’s blood group by means of a prena / harmony test.
ETS (maternal blood test + neck fold measurement)
More and more women and couples of all age groups want an early individual risk assessment for chromosomal disorders or possible malformations of their child. As the mother ages, the risk of having a child with a chromosomal disorder increases. Trisomy 21 (“Down syndrome”) occurs most frequently.
The first trimester screening includes the measurement of the neck fold (NT, fluid accumulation under the skin of the child’s neck) as well as the determination of two pregnancy-associated hormones (from the maternal blood). Taking into account the age of the mother, it allows an individual risk calculation for the presence of trisomy 21 in this pregnancy. 80% of children with trisomy 21 show a noticeable thickened NT on ultrasound. In combination with the hormone analysis, the accuracy increases to 95%. So there remains a residual risk of 5%. It should also be noted that in rare cases so-called “false positive” findings are also collected. The NT measurement can only be carried out in a narrow time frame in pregnancy from 11 + 0 to 13 + 6 weeks. This examination is carried out in a prenatal practice. According to the decision of the Federal Committee of Health Insurance Funds, the costs for this combined examination are not part of the maternity provision.
NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Test)
There are also so-called non-invasive tests for the early detection of chromosomal disorders in the child, which can be carried out from the mother by simply taking blood. In a complex process, DNA fragments from children are identified in the mother’s blood and the number of fetal chromosomes is determined. Performing the NIPT (non-invasive prenatal test) blood test for trisomy 21/18/13 as well as XO and XXY alone is currently not recommended, as the NT measurement can also indicate other non-genetic malformations. There are currently various providers on the market (e.g. PränaTest®, Harmony Test® etc.).
These tests can be taken in our practice from the 9 + 0 week of pregnancy. After about a week we will receive the test result.
Invasive diagnostics
In the event that the examinations described above produce dubious or suspicious findings or a genetic disease is suspected based on the previous history, an invasive diagnosis (chorionic villus sampling / amniocentesis = amniocentesis) in a prenatal practice is recommended. Here, the genetic information of child cells is examined genetically. 100% exclusion of a chromosomal disorder is only possible with one of these methods. There is minimal risk of miscarriage as part of the procedures.
From January 2021, a new radiation protection ordinance will come into force, which also deals with ultrasound applications in pregnant women. It is formulated as follows: “When using ultrasound devices for non-medical purposes, a fetus must not be exposed.” The aim of this new law is to ban ultrasound baby cinemas in non-medical facilities. The German Society for Ultrasound in Medicine (DEGUM) has once again confirmed that ultrasound does not pose a health risk to the fetus, does not affect fetal brain development, does not cause any secondary effects on fetal organs, and 3D / 4D ultrasound does not affect the unborn child greater risk poses.
Hardly any other medical method has been examined so thoroughly in terms of its effect as obstetric ultrasound (“evidence based medicine”). According to leading sonography experts, there is a clear connection between a higher number of ultrasound examinations and the positive outcome of the pregnancy. These additional ultrasound examinations are medically meaningful for monitoring the fetal development, but not absolutely necessary.
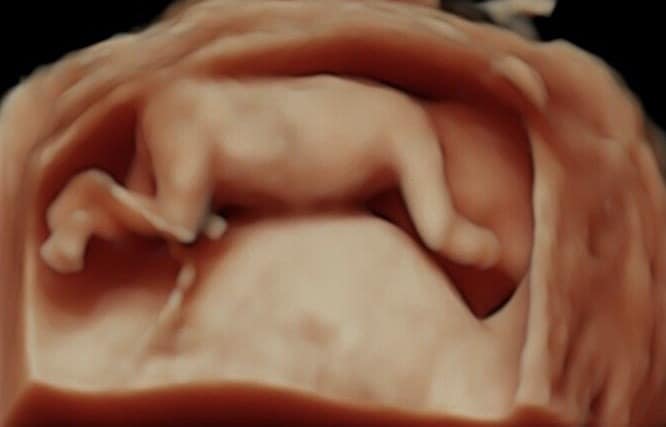
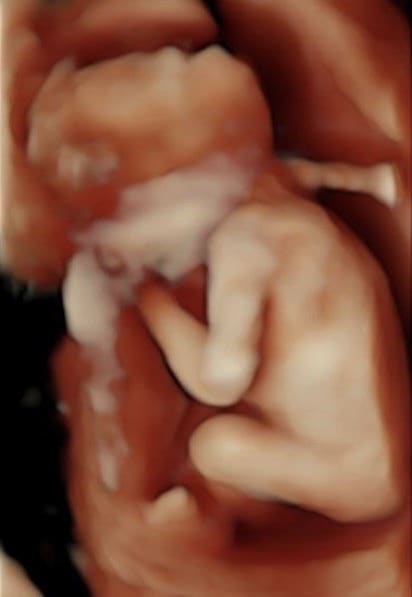
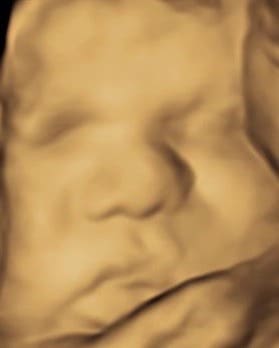
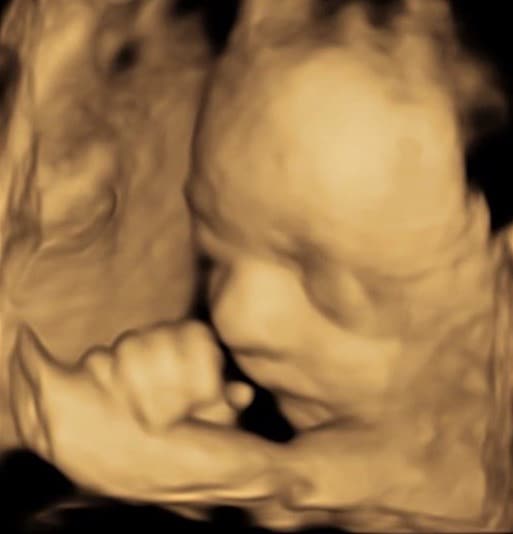
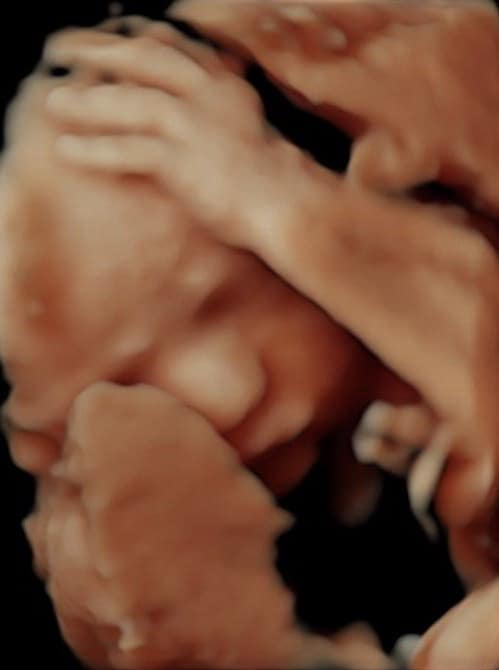
We are pleased that, in addition to conventional ultrasound examinations, we can also offer you 3- and 4-dimensional ultrasound (3D and 4D US).
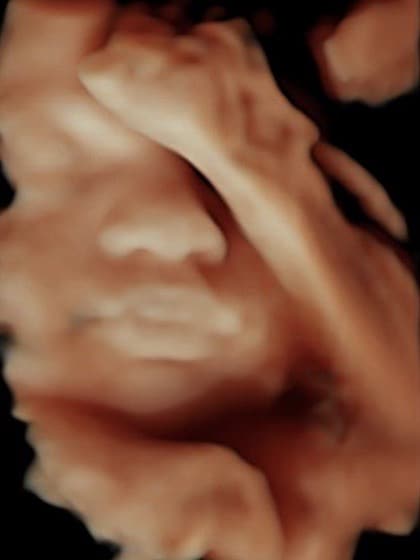
4D ultrasound is particularly impressive because we see your child vividly and in his or her movements. In this way, the fetal development of the child can be assessed even better and, above all, the morphology of the child’s face can be assessed better than with two-dimensional ultrasound. This serves to rule out cleft lip and palate. The best time for this examination is between the 26th and 32nd week of pregnancy.
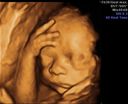
As a service of our practice, we send you ultrasound images in JPEG format via SMS or email – directly from our ultrasound devices. This requires a system that has data security criteria prescribed by law. You will receive information about how this service works during the initial consultation after it has been determined that you are pregnant.
Stem cells in the umbilical cord blood can be taken and stored in the delivery room immediately after birth. They are very valuable: Stem cells are already used in the treatment of around 80 diseases and there is active research into the further use of these cells in many medical fields.
There are non-profit and private providers for the storage of the cells. We will be happy to advise you in good time during pregnancy – if you are interested, please contact us.
Group B streptococci are found in the genital area in 20-36% of pregnant women. These bacteria are usually harmless colonists of the vaginal mucosa. However, pregnant women can infect the newborn with them at birth. As a result, the child can develop severe infections shortly after birth or after 1 to 6 weeks. The early infection is accompanied by blood poisoning (sepsis), pneumonia and meningitis. Neurological damage and long-term consequences are also to be expected with this early form. In the late form, the risk of dying from such an infection, especially in premature babies, can be very high. For these reasons, the Association of German Gynecologists has made recommendations for the prevention of this so-called neonatal B streptococcal infection.
Prevention of B streptococcal infection
A detailed survey should be carried out in advance by your doctor. Did one of your children have a B streptococcal infection after birth or have you had a urinary tract infection with B streptococci yourself? Then antibiotics should definitely be given during the birth. Otherwise, every pregnant woman between the 35th and 38th week of pregnancy should be examined for the presence of B-streptococci. All your doctor needs to do is take a vaginal rectal smear. These smears are examined in the laboratory using a bacteriological culture. If you are found to have B streptococci, antibiotics are recommended during childbirth to minimize the risk of the child becoming infected. Antibiotic therapy long before the birth is not advisable, as the B streptococci reappear relatively quickly after the end of the therapy. Also tell the clinic or your midwife if B streptococci have been found in your check-up.
Acupuncture is one of the oldest medical healing methods. Acupuncture is practically free of side effects in a trained hand, can be repeated at any time and can also be used alongside other treatment methods. It has been proven in conventional medicine that acupuncture preparatory to childbirth significantly shortens the opening phase of childbirth. We offer acupuncture once a week from the 37th week of pregnancy. During acupuncture you lie comfortably on the CTG and can take a little break for yourself and your baby.
We also offer you K-Taping® in our practice. This is an alternative treatment method in which the self-healing powers are activated and supported by different tape systems (adhesive strips).
application areas
During pregnancy / after childbirth:
- Tension of the neck muscles
- Sciatica and back problems
- Symphysis loosening
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Abdominal support
- Lochialstau
- Regression of the uterus
- Milk congestion / mastitis
- Scar tape after caesarean section
- Diastasis recti
Gynecology:
- Menstrual cramps
- Lymphatic congestion
Pregnancy timetable: the overview
|
Der „Fahrplan“ für Ihre Schwangerschaft |
Regelleistung der gesetzlichen Krankenkassen (GKV) |
Individuelle Gesundheitsleistung auf Wunsch |
|
4.-8. SSW (Schwangerschaftswoche) |
SS-Feststellung Gewicht, Blutdruck, Urin Mutterpass, Blutentnahme:
|
Arbeitsbescheinigung Toxoplasmose-Screening Zytomegalie-Screening Windpocken-Screening Parvoviren-Screening Kontrolle Schilddrüse |
|
Bis zur 30. SSW |
Kontrolle alle 4 Wochen |
|
|
9.-12. SSW |
Mutterschaftsvorsorgeuntersuchung (Muvo): Gewicht, Blutdruck, Urin, Hb I. Ultraschallscreening |
SO FRÜH WIE MÖGLICH: Anmeldung im Kreissaal und bei einer Hebamme www.hebammensuche.bayern |
|
11.-14. SSW |
Falls Mutter Rh neg, ggf RhD-NIPT. Ggf NIPT als Kassenleistung |
Früher pränataler Ultraschall NIPT Zusatzuntersuchungen auf Wunsch |
|
14.-16. SSW |
Muvo |
Ultraschall (evtl Geschlechtsbestimmung) |
|
19.-22. SSW |
Muvo II. Ultraschallscreening saisonal Grippeimpfung |
Toxoplasmose-/Zytomegalie-/Toxoplasmose- Screening |
|
23.-29. SSW |
Muvo Tokogramm (Wehenschreiber) Antikörpersuchtest ggf Rhesusprophylaxe (bei Rh -) ab 24+0: 50g Zuckerbelastungstest 1h danach evtl 75g OGTT (nüchtern! 2 h) |
Ultraschall 3D Ultraschall Bei Beschwerden Akupunktur / Aku-Taping Info Nabelschnurblutspende |
|
29.-32. SSW |
Muvo + CTG (Wehenschreiber + Herztöne) Pertussisimpfung III. Ultraschallscreening |
Toxoplasmose-Screening Zytomegalie-Screening |
|
Ab der 30. SSW |
Kontrolle alle 2 Wochen |
|
|
32.-40. SSW |
Muvo CTG 1x Hepatitis B-Untersuchung (Hbs-AG) |
Ultraschall 3D Ultraschall Streptokokkenabstrich (vaginal) Akupunktur Akutaping |
|
Am Termin (ET) |
Muvo CTG Fruchtwaserkontrolle |
Ultraschall |
|
Nach dem Termin |
CTG und evtl Fruchtwasserkontrolle alle 2 Tage |


 Deutsch
Deutsch